
4340 Alloy steel | 34CrNiMo6 | 1.6582
AOBO STEEL – Trusted Global Tool Steel Supplier
4340 alloy steel is a prominent type of medium-carbon low-alloy steel and is recognized as an ultrahigh-strength steel. It is often considered the standard against which other ultrahigh-strength steels are compared. The UNS (Unified Numbering System) designation for 4340 alloy steel is G43400. Internationally, it corresponds to standards like SNB23-1-5 or SNB24-1-5 in Japan, and 34CrNiMo6 in Europe. It is also identified by the AMS (Aerospace Material Specification) number 6414.
1. Applications
Aircraft and Aerospace: Aircraft parts. Aircraft landing gear. Airframe parts. Connecting rods
Machinery Components: Gears. Pinions. Shafts. Crankshafts and piston rods for engines. Splines
Fasteners: Bolts. Screws. Studs
Structural Components: Pressure vessels. Mountain bicycle frames
2. 4340 Steel Composition1
| Carbon (C) | Chromium (Cr) | Nickel (Ni) | Molybdenum (Mo) | Manganese (Mn) | Silicon (Si) | Phosphorus (P) | Sulfur (S) |
| 0.38 – 0.43% | 0.70 – 0.90% | 1.65 – 2.00% | 0.20 – 0.30% | 0.60 – 0.80% | 0.20 – 0.35% | ≤ 0.035% (max) | ≤ 0.040% (max) |
3. 4340 Alloy Steel Properties
3.1 Mechanical Properties
4340 alloy steel exhibits excellent strength, good ductility, and outstanding toughness, as well as resistance to fatigue and creep. Its tempering properties after quenching are roughly equivalent to those of carbon steel. Mechanical properties are greatly influenced by the tempering temperature after oil quenching.
The following table lists the 4340 steel material properties in different oil quenching and tempering conditions.
| Tempering Temperature | Tensile Strength (MPa / ksi) | Yield Strength (MPa / ksi) | Hardness (HB / HRC) | Impact Toughness |
| 205°C (400°F) | ~1980 / ~287 | ~1860 / ~270 | ~520HB / ~53HRC | Relatively Lower |
| 425°C (800°F) | ~1500 / ~217 | ~1365 / ~198 | ~440HB / ~46HRC | Moderate |
| 540°C (1000°F) | ~1150 / ~167 | ~1050 / ~152 | ~360HB/~39HRC | Notably Higher |
| 650°C (1200°F) | ~1020 / ~148 | ~860 / ~125 | ~290HB / ~31HRC | High |
After quenching and tempering, AISI 4340 alloy steel forms a lath martensite microstructure. During rapid cooling, the formation of martensite is accompanied by volume expansion. Depending on the cooling rate, other microstructures, such as bainite, may also form.
3.2 Machinability
The machinability of steel AISI 4340 is generally rated at 55% for cold-drawn material and 45% for annealed material, relative to B1112 steel (rated at 100%). For optimal machinability, a partly spheroidized microstructure, achieved by normalizing followed by tempering, is recommended.
3.3 Weldability
4340 steel has excellent weldability and can be joined using gas or arc welding processes. However, as an air-hardening steel, it also requires certain protective measures. AISI 4340 steel is more difficult to weld than ordinary carbon steel, and preheating the material and controlling the interpass temperature are necessary during welding. Additionally, annealing or normalizing treatment followed by tempering should be performed as soon as possible after welding.
3.4 Nitriding
AISI 4340 can be readily nitrided, and this process often improves its fatigue life. While 4140 steel, because of its higher chromium content and nickel-free composition, generally exhibits superior nitriding characteristics, 4340 still develops a heavier nitrided case than 8640 steel during the initial 24 hours of nitriding. Typical nitriding temperatures for 4340 steel range from 510 to 550 °C (950 to 1020 °F). Based on our customers’ applications of nitrided 4340 steel for gear manufacturing, the core hardness is typically 38-42 HRC.
3.5 Potential Issues and Processing Precautions
Users of material 4340 should be aware of potential challenges:
- Cracking: Water quenching significantly increases the risk of cracking.
- Hydrogen Embrittlement: This can be a concern when the steel is heat-treated to very high tensile strengths (above approximately 1400 MPa / 200 ksi). We suggest baking after processes like pickling or plating.
- Stress-Corrosion Cracking: AISI 4340 steel shows poor resistance to stress-corrosion cracking, particularly when tempered to high tensile strengths (1500 to 1950 MPa / 220 to 280 ksi).
- Intergranular Fracture: Susceptibility is influenced by impurities and the presence of hydrogen.
- Temper Embrittlement: This is a known phenomenon for this alloy.

Are you seeking a reputable supplier of 4340 alloy steel?
Please fill out the following form to contact us now!
4. Heat Treatment
The heat treatment of 4340 steel involves several key processes, each influencing its final microstructure and mechanical properties:
4.1 Forging
The forging temperature is 1065 to 1230°C (1950 to 2250°F). After the forging process, parts can be air-cooled in a dry environment or, preferably, furnace-cooled. The flow stress of 4340 steel can increase by approximately 15% with a 55 °C (100 °F) drop in hot forging temperature.
4.2 Normalizing
Normalizing can improve the microstructure of 4340 steel after uneven cooling at high temperatures. This process is also applicable to alloy steel forgings, rolled products, and castings.
Heat 4340 steel to a temperature 55 to 85°C (100 to 150°F) above its phase transformation temperature (845 to 900°C, or 1550 to 1650°F), at which the original microstructure is completely dissolved into austenite. The material is then cooled to room temperature in air.
4.3 Annealing
The annealing temperature for 4340 steel is 790-845 °C (1450-1550 °F), with a maximum 4340 steel hardness of 223 HB after annealing.
4.4 Hardening (Quenching)
Heat 4340 steel to its austenitic transformation temperature of 800 to 845°C (1475 to 1550°F). We usually select an austenitizing temperature of 845°C (1550°F). Soak for approximately 15 minutes per 25 mm (1 inch) of section size, with a minimum hold time of 150 minutes, followed by annealing. For thin-section 4340 steel, annealing is performed by air annealing. For circular sections with a diameter not exceeding 75 mm (3 inches), oil quenching may be used.
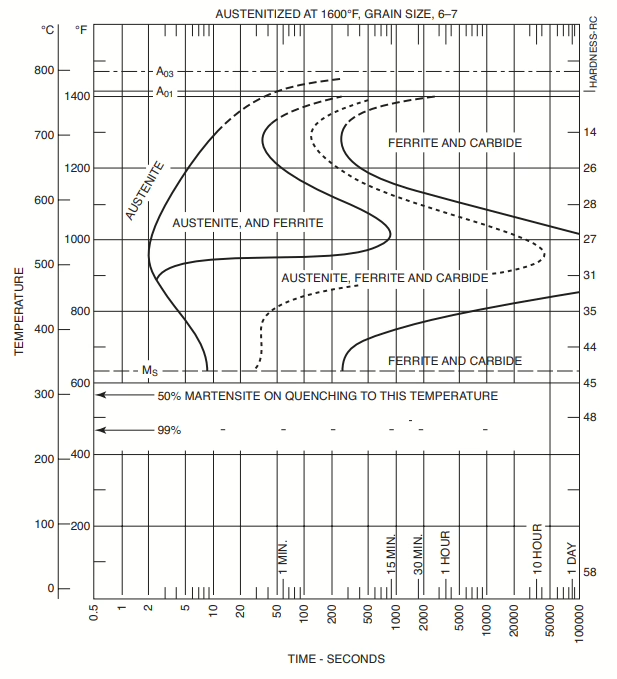
Isothermal transformation diagram for a 4340 steel containing 0.42% C, 0.78% Mn, 1.79% Ni, 0.80% Cr, and 0.33% Mo. [Source: From The Making, Shaping and Treating of Steels, 9th ed., ibid.]
4.5 Tempering
Tempering effectively reduces the brittleness of untempered martensite. Tempering temperatures range from 200 to 650°C (400 to 1200°F) to achieve the required strength levels, and can even reach as high as 705°C (1300°F).
For AISI 4340 steel oil-quenched at 845°C (1550°F), we strongly recommend a tempering temperature of 425°C (800°F), while for water-quenched 4340 steel, we strongly recommend a tempering temperature of 650°C (1200°F).
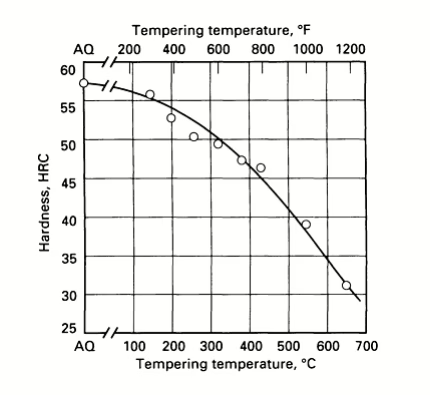
Variation in hardness with tempering temperature of 4340 steel. All specimens oil quenched from 845 °C (1550 °F) and tempered 2 h at temperature. AQ, as-quenched. [Source: ASM International. (1991). ASM Handbook, Volume 4: Heat Treating (p. 506). ASM International.]
4.6 Stress Relieving
This step is designed to reduce residual stress generated by processes such as straightening, forming, or machining. Stress relief for 4340 steel is performed before hardening at a temperature of 650 to 675 °C (1200 to 1250 °F). For hardened 4340 material, the stress relief temperature should not exceed the previous tempering temperature.
4.7 Spheroidizing
The purpose of spheroidizing treatment is to form a spheroidal carbide microstructure in the ferritic matrix, which softens the steel. The maximum temperature for spheroidizing treatment of 4340 steel is 760-775°C (1400-1425°F). A semi-spheroidized structure is obtained by normalizing, followed by tempering at 650°C (1200°F).
5. 4340 Steel Equivalent Grades
| Country/Region | Equivalent Grade |
| America | AISI/SAE 4340 |
| Japan | JIS SNCM439 |
| China | GB 40CrNiMoA |
| EU | EN 34CrNiMo6 (1.6582) |
- ASM International. (1991). ASM Handbook, Volume 4: Heat Treating (p. 496). ASM International. ↩︎
FAQ
1. Is 4340 the strongest steel?
AISI/SAE 4340 steel is indeed a very strong and widely recognized material within the category of ultrahigh-strength steels. However, 4340 is not definitively the strongest steel available.
2. Is 4340 steel or aluminum?
4340 is a type of steel, not aluminum.
3. Can 4340 steel be hardened?
Yes, 4340 steel can indeed be hardened, and it is specifically known as a deep-hardening steel
4. Is 4340 steel good for knives?
4340 steel is commonly used for highly stressed components in machinery and aircraft, not for knives.
5. Is 4340 steel martensitic?
Yes, 4340 steel is a martensitic alloy steel. It is designed and commonly heat-treated to form a martensitic microstructure.
6. What is the difference between 4140 and 4340?
The key distinction between 4140 and 4340 steel is the presence of a significant amount of nickel (Ni) in 4340, which is generally absent in 4140. This nickel addition provides 4340 with superior hardenability and toughness, making it suitable for applications requiring ultra-high strength and improved fracture toughness. While 4140 has good strength and hardenability, it is not a deep-hardening steel. Despite 4340’s overall higher performance, 4140 is noted for better nitriding characteristics due to its nickel-free composition and higher chromium content.
Unlock the Potential of 4340 Alloy Steel for Your Project
Experience the superior strength, toughness, and versatility of AISI 4340 alloy steel. Whether you require high-performance components for aerospace, automotive, or heavy machinery, our 4340 steel meets the most demanding specifications.
Ready to discuss your requirements or get a quote? Our experts are here to help you find the perfect 4340 steel solution.
Fill out the form below, and one of our specialists will contact you shortly.
Explore Our Other Products
D2/1.2379/SKD11
D3/1.2080/SKD1
D6/1.2436/SKD2
A2/1.23663/SKD12
O1/1.2510/SKS3
O2/1.2842
S1/1.2550
S7/1.2355
DC53
H13/1.2344/SKD61
H11/1.2343/SKD6
H21/1.2581/SKD7
L6/1.2714/SKT4
M2/1.3343/SKH51
M35/1.3243/SKH55
M42/1.3247/SKH59
P20/1.2311
P20+Ni/1.2738
420/1.2083/2Cr13
422 stainless steel
52100 bearing steel
440C stainless steel
4140/42CrMo4/SCM440
4340/34CrNiMo6/1.6582
4130
5140/42Cr4/SCR440
SCM415
