When choosing the right tool steel for your project, you may come across D2 and D3 tool steels. Both tool steels are high-carbon, high-chromium tool steels that are widely used in the tool and die industry for cold work tools such as cutting tools, dies and punches. They are classified as D series in the AISI classification system and were originally developed as potential replacements for HSS, but were not widely used at high temperatures due to their lack of hot hardness and brittleness when machined. Nonetheless, D2 and D3 tool steels exhibit excellent wear resistance in cold working applications due to the large volume fraction of cemented carbides formed from the high carbon and chromium content. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the differences between these two materials to help you choose the tool steel that best suits your project’s needs.


Chemical composition comparison
The carbon and chromium content in D2 and D3 steels are critical to their performance. As shown in the table below, D2 has a carbon content of 1.40-1.60% and chromium content of 11.00-13.00%, while D3 has a higher carbon content of 2.00-2.35% and a similar chromium content of 11.00-13.50%. This high chromium content enhances their good corrosion resistance, while the carbon content boosts their hardness and wear resistance due to the formation of carbides. It should be noted that none of them are stainless steel.
| AISI Type | UNS No. | C (%) | Mn (%) | Si (%) | Cr (%) | Ni (%) | Mo (%) | V (%) |
| D2 | T30402 | 1.40-1.60 | 0.60 max | 0.60 max | 11.00-13.00 | 0.30 max | 0.70-1.20 | 1.10 max |
| D3 | T30403 | 2.00-2.35 | 0.60 max | 0.60 max | 11.00-13.50 | 0.30 max | … | … |
Major factors comparison
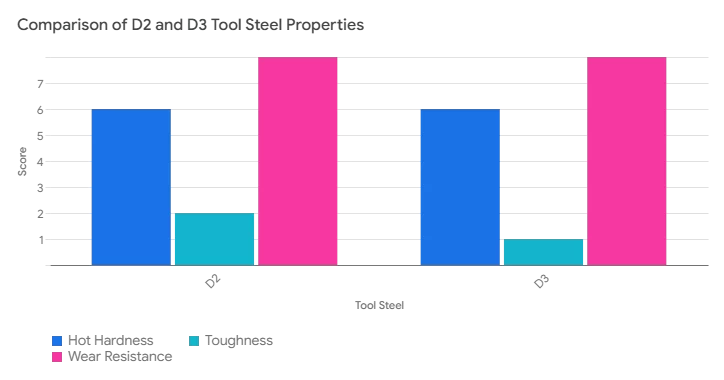
The table compares D2 and D3 in hot Hardness, toughness, and wear Resistance. Each figure is scored out of 10. From the table, we can see that both D2 and D3 have excellent wear resistance and moderate hot hardness but are worse in terms of toughness.
Manufacturing factors comparison
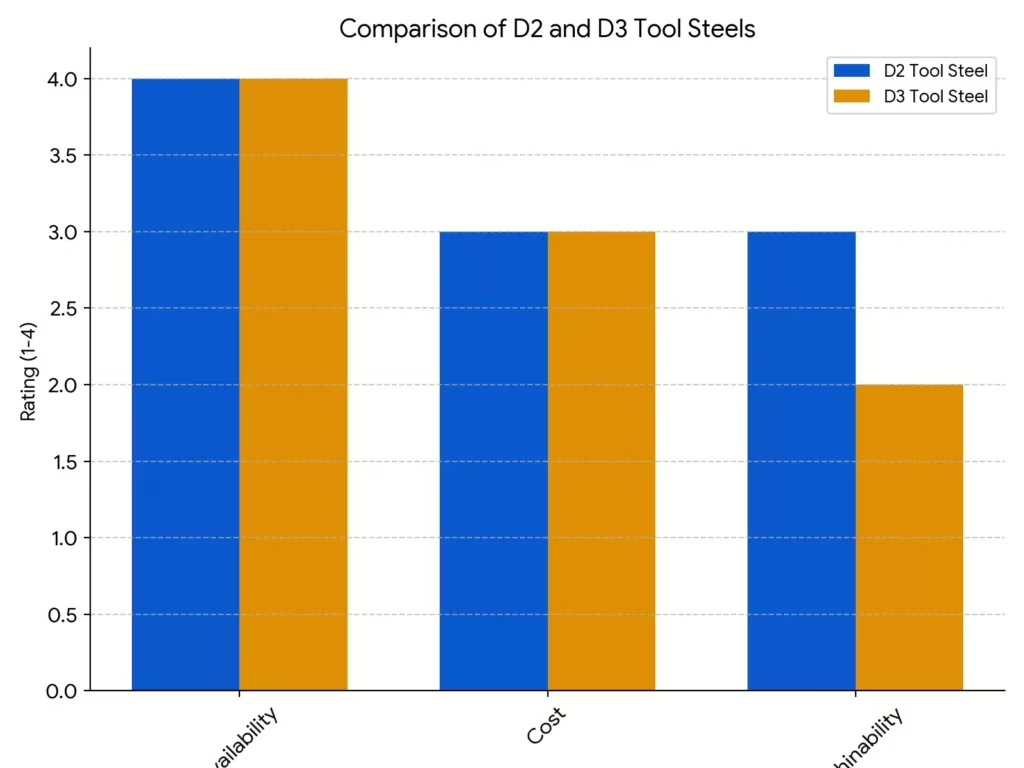
Compare D2 and D3 based on their availability, cost, and machinability. The vertical axis shows their scores on this item, out of 10.
D2 vs. D3 tool steel Comparison of other parameters
The properties of D2 and D3 steels are significantly influenced by heat treatment, particularly the hardening and tempering processes, which optimize their hardness and durability. The table below compares various parameters related to their heat treatment and resulting properties.
| Factor | D2 | D3 |
| Usual Working Hardness, HRC | 58-64 | 58-64 |
| Depth of Hardening | D | D |
| Finest Grain Size at Full Hardness, Shepherd Standard | 7 1/2 | 7 1/2 |
| Surface Hardness as-Quenched, HRC | 61-64 | 64-66 |
| Core Hardness (25 mm or 1 in. diam round), HRC | 61-64 | 64-66 |
| Quenching Medium | A | O |
| Hardening Temperature, °C (°F) | 980-1025 (1800-1875) | 925-980 (1700-1800) |
| Dimensional Change on Hardening | L | L |
| Safety on Hardening | H | M |
| Susceptibility to Decarburization | H | H |
| Approximate Hardness as-Rolled or Forged, HB | 550 | 400 |
| Annealed Hardness, HB | 217-255 | 217-255 |
| Annealing Temperature, °C (°F) | 870-900 (1600-1650) | 870-900 (1600-1650) |
| Tempering Range, °C (°F) | 205-540 (400-1000) | 205-540 (400-1000) |
| Forging Temperature, °C (°F) | 1010-1095 (1850-2000) | 1010-1095 (1850-2000) |
Compressive Strengths of D2 and D3 tool steels after hardening to maximum hardness and tempering at temperatures noted
The compressive strength of D2 and D3 tool steels varies with heat treatment, specifically the tempering temperature, as shown in the table below.
| Steel | Tempering Temperature (°C) | Tempering Temperature (°F) | Hardness (HRC) | Ultimate Compressive Strength (MPa) | Ultimate Compressive Strength (ksi) |
| D2 | 175 | 350 | 61.5 | 3841 | 557 |
| D2 | 230 | 450 | 59.5 | 3641 | 528 |
| D3 | 175 | 350 | 63.5 | 3634 | 527 |
| D3 | 230 | 450 | 61.5 | 3290 | 477 |
Application comparison
The high carbon high chromium D-type steels are divided into two groups according to carbon content. D3 steel offers the highest wear resistance but with low toughness, belonging to high-carbon steel (including D4 and D7). D2 belongs to low-carbon steel (including D5), which has relatively high wear resistance and slightly higher toughness than D-type steels with a carbon content of 2% or more. High-carbon steel can be chosen instead of D2 if a longer production cycle is expected. However, high-carbon steel is more difficult to process. D2 steel is sometimes used for hot trimming of forgings, but high carbon high chromium steels are primarily used for cold working tools in the tool and die industry, such as cutting tools for sheet metal, where excellent wear resistance is essential.


