Wybierając odpowiednią stal narzędziową do swojego projektu, możesz natknąć się na Stal narzędziowa D2 I Stal narzędziowa D3Obie stale narzędziowe to stale narzędziowe wysokowęglowe i wysokochromowe, szeroko stosowane w przemyśle narzędziowym i matrycowym do obróbki na zimno, takie jak narzędzia skrawające, matryce i stemple. Są one klasyfikowane jako seria D. AISI System klasyfikacji stali narzędziowych D2 i D3 został opracowany jako potencjalny zamiennik stali szybkotnącej (HSS), ale nie był szeroko stosowany w wysokich temperaturach ze względu na brak twardości na gorąco i kruchość podczas obróbki skrawaniem. Niemniej jednak stale narzędziowe D2 i D3 wykazują doskonałą odporność na zużycie w obróbce na zimno dzięki dużej zawartości węglików spiekanych, które powstają z wysokiej zawartości węgla i chromu. W tym artykule przyjrzymy się bliżej różnicom między tymi dwoma materiałami, aby pomóc Ci wybrać stal narzędziową najlepiej odpowiadającą potrzebom Twojego projektu.


Porównanie składu chemicznego
Zawartość węgla i chromu w stalach D2 i D3 ma kluczowe znaczenie dla ich właściwości użytkowych. Jak pokazano w poniższej tabeli, stal D2 charakteryzuje się zawartością węgla na poziomie 1,40–1,60% i chromu na poziomie 11,00–13,00%, natomiast stal D3 charakteryzuje się wyższą zawartością węgla na poziomie 2,00–2,35% i podobną zawartością chromu na poziomie 11,00–13,50%. Wysoka zawartość chromu poprawia ich odporność na korozję, a zawartość węgla zwiększa ich twardość i odporność na zużycie dzięki tworzeniu się węglików. Należy zauważyć, że żadna z tych stali nie jest stalą nierdzewną.
| AISI | Numer UNS | C (%) | Mn(%) | Si (%) | Cr (%) | Ni (%) | Mo (%) | W (%) |
| D2 | T30402 | 1.40-1.60 | 0,60 maks. | 0,60 maks. | 11.00-13.00 | 0,30 maks. | 0.70-1.20 | 1,10 maks. |
| D3 | T30403 | 2.00-2.35 | 0,60 maks. | 0,60 maks. | 11.00-13.50 | 0,30 maks. | … | … |
Porównanie głównych czynników
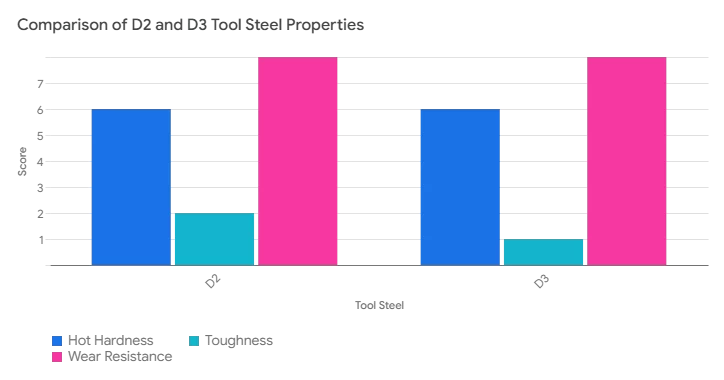
Tabela porównuje D2 i D3 pod względem twardości na gorąco, wytrzymałości i odporności na zużycie. Każda wartość jest punktowana w skali 1-10. Z tabeli wynika, że zarówno D2, jak i D3 charakteryzują się doskonałą odpornością na zużycie i umiarkowaną twardością na gorąco, ale są gorsze pod względem wytrzymałości.
Porównanie czynników produkcyjnych
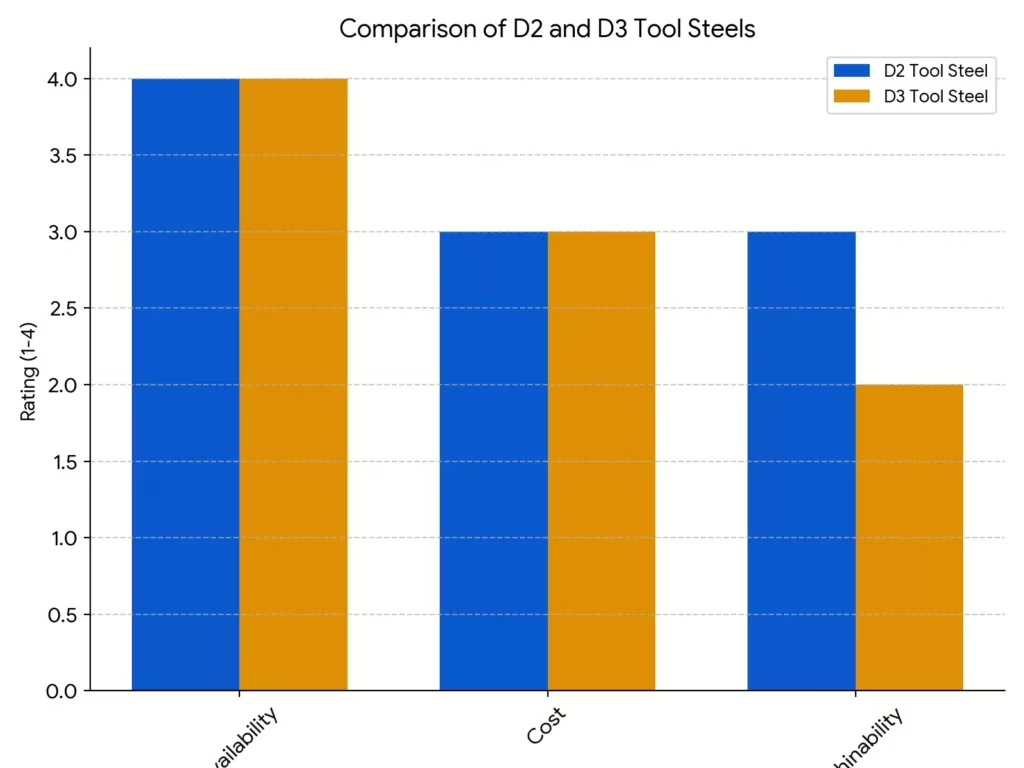
Porównaj D2 i D3 na podstawie ich dostępności, kosztów i obrabialności. Oś pionowa pokazuje ich wyniki dla tego elementu, w skali od 1 do 10.
Stal narzędziowa D2 vs. D3 Porównanie innych parametrów
Właściwości stali D2 i D3 są znacząco modyfikowane przez obróbkę cieplną, w szczególności przez procesy hartowania i odpuszczania, które optymalizują ich twardość i trwałość. Poniższa tabela porównuje różne parametry związane z ich obróbką cieplną i wynikającymi z niej właściwościami.
| Czynnik | D2 | D3 |
| Zwykła twardość robocza, HRC | 58-64 | 58-64 |
| Głębokość hartowania | D | D |
| Najdrobniejszy rozmiar ziarna przy pełnej twardości, standard Shepherd | 7 1/2 | 7 1/2 |
| Twardość powierzchni po hartowaniu, HRC | 61-64 | 64-66 |
| Twardość rdzenia (średnica 25 mm lub 1 cal okrągły), HRC | 61-64 | 64-66 |
| Medium hartujące | A | O |
| Temperatura utwardzania, °C (°F) | 980-1025 (1800-1875) | 925-980 (1700-1800) |
| Zmiana wymiarów podczas hartowania | L | L |
| Bezpieczeństwo podczas hartowania | H | M |
| Podatność na odwęglanie | H | H |
| Przybliżona twardość po walcowaniu lub kuciu, HB | 550 | 400 |
| Twardość wyżarzana, HB | 217-255 | 217-255 |
| Temperatura wyżarzania, °C (°F) | 870-900 (1600-1650) | 870-900 (1600-1650) |
| Zakres temperowania, °C (°F) | 205-540 (400-1000) | 205-540 (400-1000) |
| Temperatura kucia, °C (°F) | 1010-1095 (1850-2000) | 1010-1095 (1850-2000) |
Wytrzymałość na ściskanie stali narzędziowych D2 i D3 po hartowaniu do maksymalnej twardości i odpuszczaniu w podanych temperaturach
Wytrzymałość na ściskanie Stale narzędziowe D2 i D3 zmienia się w zależności od obróbka cieplna, a konkretnie temperatura odpuszczania, jak pokazano w poniższej tabeli. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na ten temat, zapoznaj się z Obróbka cieplna stali narzędziowej D2 i Obróbka cieplna stali narzędziowej D3.
| Stal | Temperatura odpuszczania (°C) | Temperatura hartowania (°F) | Twardość (HRC) | Maksymalna wytrzymałość na ściskanie (MPa) | Wytrzymałość na ściskanie (ksi) |
| D2 | 175 | 350 | 61.5 | 3841 | 557 |
| D2 | 230 | 450 | 59.5 | 3641 | 528 |
| D3 | 175 | 350 | 63.5 | 3634 | 527 |
| D3 | 230 | 450 | 61.5 | 3290 | 477 |
Porównanie aplikacji
Stale wysokowęglowe i wysokochromowe typu D dzielą się na dwie grupy według zawartości węgla. Stal D3 oferuje najwyższą odporność na zużycie, ale przy niskiej ciągliwości, należąc do stali wysokowęglowych (w tym D4 i D7). D2 należy do stali niskowęglowych (w tym D5), która ma stosunkowo wysoką odporność na zużycie i nieco wyższą ciągliwość niż stale typu D o zawartości węgla 2% lub wyższej. Stal wysokowęglową można wybrać zamiast D2, jeśli przewidywany jest dłuższy cykl produkcyjny. Jednak stal wysokowęglowa jest trudniejsza w obróbce. Stal D2 jest czasami używana do gorącego przycinania odkuwek, ale stale wysokowęglowe i wysokochromowe są używane przede wszystkim do narzędzi do obróbki na zimno w przemyśle narzędziowym i matrycowym, takich jak narzędzia skrawające do blach, gdzie doskonała odporność na zużycie jest niezbędna.
Uzyskaj konkurencyjną ofertę na stal narzędziową D2/D3
Z ponad 20-letnim doświadczeniem w kuciu, Aobo Steel jest Twoim zaufanym partnerem w zakresie wysokowydajnej stali narzędziowej D2/D3. Dostarczamy nie tylko materiały, ale i rozwiązania. Wykorzystaj naszą dogłębną wiedzę branżową i niezawodny łańcuch dostaw, aby Twój projekt odniósł sukces.
✉ Skontaktuj się z nami wypełniając poniższy formularz.


