Při výběru správné nástrojové oceli pro váš projekt můžete narazit Nástrojová ocel D2 a Nástrojová ocel D3. Both tool steels are high-carbon, high-chromium tool steels that are widely used in the tool and die industry for cold work tools such as cutting tools, dies, and punches. They are classified as D series in the AISI classification system and were initially developed as potential replacements for HSS, but were not widely used at high temperatures because of their lack of hot hardness and brittleness when machined. Nonetheless, D2 and D3 tool steels exhibit excellent wear resistance in cold working applications because of the large volume fraction of cemented carbides formed from the high carbon and chromium content. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the differences between these two materials to help you choose the tool steel that best suits your project’s needs.


Srovnání chemického složení
The carbon and chromium content in D2 and D3 steels is critical to their performance. As shown in the table below, D2 has a carbon content of 1.40-1.60% and chromium content of 11.00-13.00%, while D3 has a higher carbon content of 2.00-2.35% and a similar chromium content of 11.00-13.50%. This high chromium content enhances their good corrosion resistance, while the carbon content boosts their hardness and wear resistance due to the formation of carbides. It should be noted that none of them is stainless steel.
| AISI | UNS č. | C (%) | Mn (%) | Si (%) | Cr (%) | Ni (%) | Po (%) | V (%) |
| D2 | T30402 | 1.40-1.60 | 0,60 max | 0,60 max | 11.00-13.00 | 0,30 max | 0.70-1.20 | 1,10 max |
| D3 | T30403 | 2.00-2.35 | 0,60 max | 0,60 max | 11.00-13.50 | 0,30 max | … | … |
Porovnání hlavních faktorů
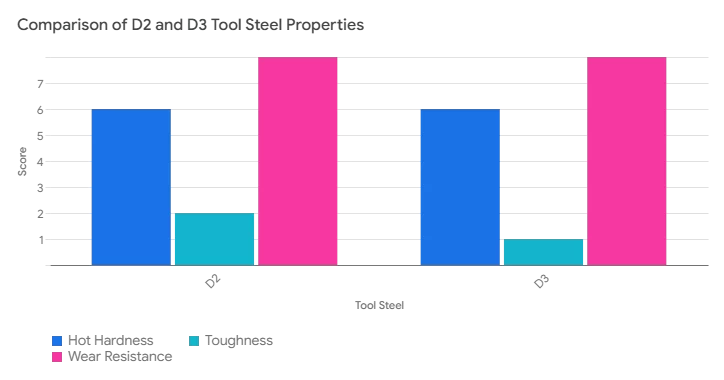
The table compares D2 and D3 in hot-hardness, toughness, and wear Resistance. Each figure is scored out of 10. From the table, we can see that both D2 and D3 have excellent wear resistance and moderate hot hardness, but are worse in terms of toughness.
Srovnání výrobních faktorů
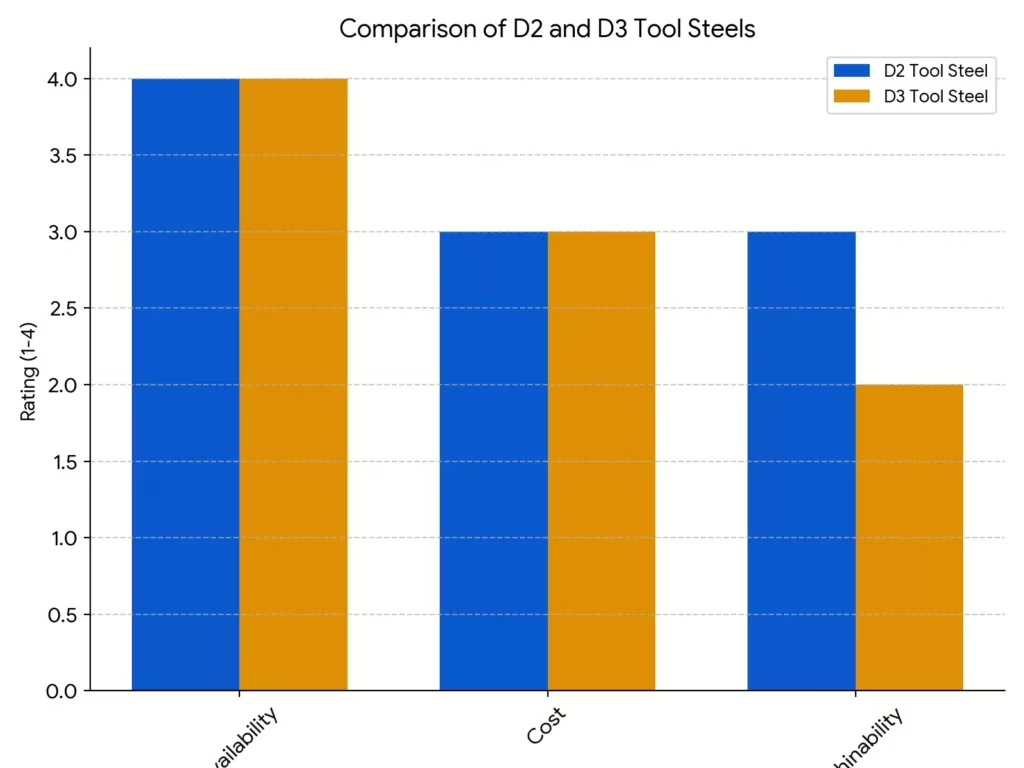
Porovnejte D2 a D3 na základě jejich dostupnosti, nákladů a obrobitelnosti. Svislá osa ukazuje jejich skóre u této položky z 10.
Nástrojová ocel D2 vs. D3 Porovnání ostatních parametrů
Vlastnosti ocelí D2 a D3 významně ovlivňuje tepelné zpracování, zejména procesy kalení a popouštění, které optimalizují jejich tvrdost a trvanlivost. Níže uvedená tabulka porovnává různé parametry související s jejich tepelným zpracováním a výslednými vlastnostmi.
| Faktor | D2 | D3 |
| Obvyklá pracovní tvrdost, HRC | 58-64 | 58-64 |
| Hloubka kalení | D | D |
| Nejjemnější velikost zrna při plné tvrdosti, Shepherd Standard | 7 1/2 | 7 1/2 |
| Tvrdost povrchu po kalení, HRC | 61-64 | 64-66 |
| Tvrdost jádra (25 mm nebo 1 in. průměr kulaté), HRC | 61-64 | 64-66 |
| Kalící médium | A | Ó |
| Teplota kalení, °C (°F) | 980-1025 (1800-1875) | 925-980 (1700-1800) |
| Změna rozměrů při kalení | L | L |
| Bezpečnost při kalení | H | M |
| Náchylnost k oduhličení | H | H |
| Přibližná tvrdost válcovaná nebo kovaná, HB | 550 | 400 |
| Tvrdost žíhaná, HB | 217-255 | 217-255 |
| Teplota žíhání, °C (°F) | 870-900 (1600-1650) | 870-900 (1600-1650) |
| Rozsah temperování, °C (°F) | 205-540 (400-1000) | 205-540 (400-1000) |
| Teplota kování, °C (°F) | 1010-1095 (1850-2000) | 1010-1095 (1850-2000) |
Pevnost v tlaku nástrojových ocelí D2 a D3 po kalení na maximální tvrdost a popouštění při uvedených teplotách
Pevnost v tlaku Nástrojové oceli D2 a D3 se liší s tepelné zpracování, specifically the tempering temperature, as shown in the table below. For more information on this topic, please refer to the Tepelné zpracování nástrojové oceli D2 and the D3 tool steel heat treatment.
| Ocel | Teplota temperování (°C) | Teplota temperování (°F) | Tvrdost (HRC) | Maximální pevnost v tlaku (MPa) | Maximální kompresní síla (ksi) |
| D2 | 175 | 350 | 61.5 | 3841 | 557 |
| D2 | 230 | 450 | 59.5 | 3641 | 528 |
| D3 | 175 | 350 | 63.5 | 3634 | 527 |
| D3 | 230 | 450 | 61.5 | 3290 | 477 |
Srovnání aplikací
The high-carbon, high-chromium D-type steels are divided into two groups according to carbon content. D3 steel offers the highest wear resistance but with low toughness, belonging to high-carbon steel (including D4 and D7). D2 belongs to low-carbon steel (including D5), which has relatively high wear resistance and slightly higher toughness than D-type steels with a carbon content of 2% or more. High-carbon steel can be chosen instead of D2 if a longer production cycle is expected. However, high-carbon steel is more difficult to process. D2 steel is sometimes used for hot trimming of forgings, but high carbon, high chromium steels are primarily used for cold working tools in the tool and die industry, such as cutting tools for sheet metal, where excellent wear resistance is essential.
Get a Competitive Quote for D2/D3 Tool Steel
With over 20 years of forging expertise, Aobo Steel is your trusted partner for high-performance D2/D3 tool steel. We provide not just materials, but solutions. Leverage our deep industry knowledge and reliable supply chain for your project’s success.
✉ Kontaktujte nás vyplněním níže uvedeného formuláře.


